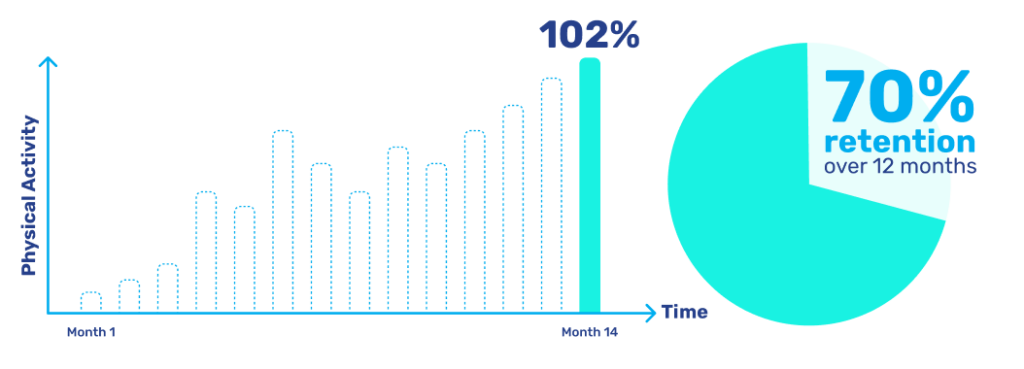
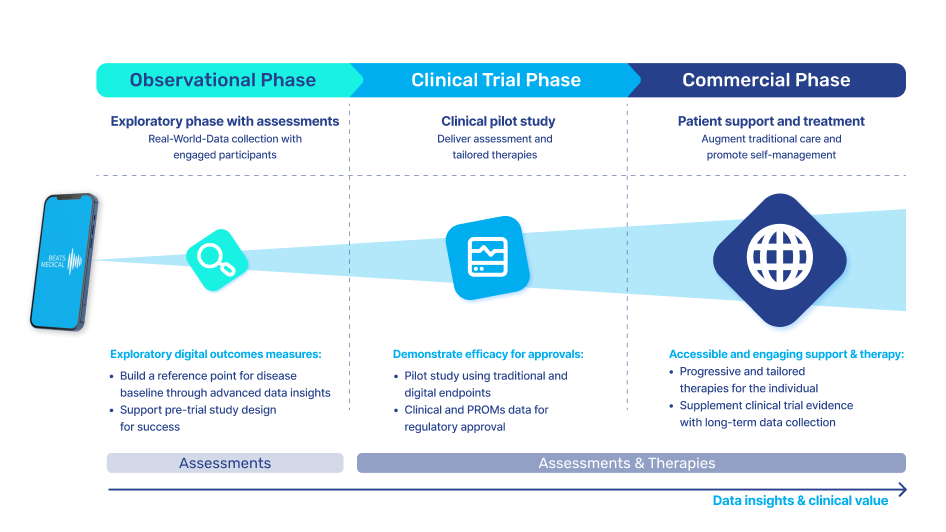
Insider Insights: Our Top 4 Industry Trends Defining 2024
Published on February 7, 2024

2024 will be a transformative year for the pharmaceutical industry and for digital health. The convergence between the two spaces is an obvious inflexion point, which can drive real impact for patients around the world.
The pharmaceutical industry, which has at times been slow in embracing innovation, is now adopting a more open approach to digitally enabled trials, especially where AI is concerned. Similarly, following some high-profile setbacks for digital health champions in 2023, the industry is finding its place in pharma’s R&D pipeline.
With the rapid pace of innovation in areas like AI, where new advancements and announcements break almost daily, predicting trends and milestones for the industry can be speculative. However, as the conversation around pharma and digital continues, key trends such as Generative AI, precision medicine, RWE and decentralised trials prevail. As we dive into 2024, I believe four key trends will reshape the landscape for digital health, and how it facilitates pharma in delivering new therapeutic breakthroughs for patients like never before.
1. Novel pharma and digital partnerships
In 2023, the Digital Therapeutics (DTx) industry faced public setbacks, notably front-runner Pear Therapeutic’s unfortunate outcome, resulting in a pivot in the market. The visionary goal of reshaping how payers provide and reimburse care stalled, with Prescription DTx hitting roadblocks in adoption. Despite positive progress in DTx coverage (most notably in Asia with Japan and South Korea making real strides), the payer market is still in a learning phase, establishing a benchmark for digital therapeutics against the standard of care. Ultimately, this means that both DTx and pharma need to find an alternative way of collaborating that delivers value on both sides and most importantly to patients.
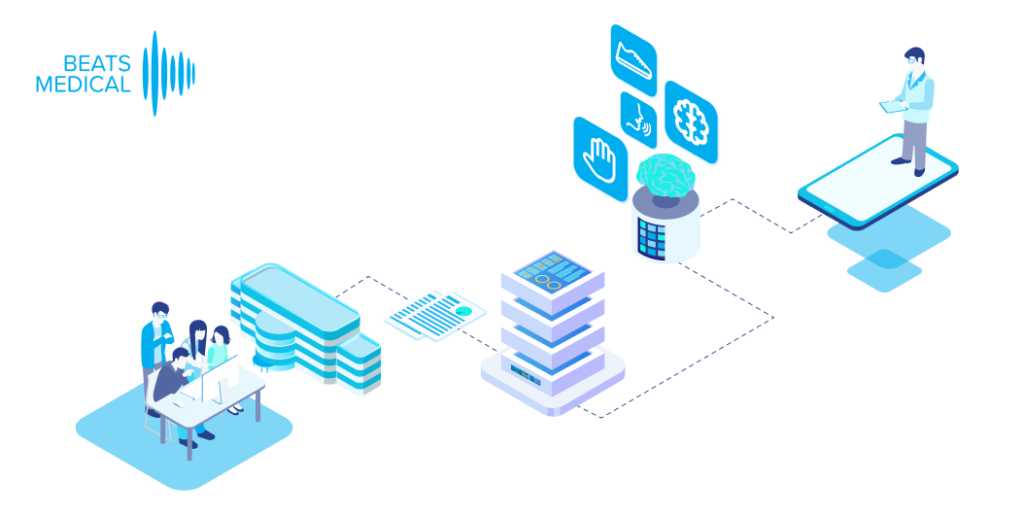
In 2024, I anticipate the most fruitful collaboration between pharma and digital to be in the R&D business. Facing rising pressure to increase clinical trial effectiveness, reduce operational costs, and offer low-friction participation to patients, pharma must embrace technology in the clinical trial pipeline. Efforts to widen access at the top of the recruitment funnel, along with the need for more sensitive longitudinal data will drive the adoption of digital assessment and measurement tools. Those with a centralised focus, partnering with platforms that can deploy digital measures to multiple investigational assets, with common symptoms or outcome measures, will see real returns in their pipeline. Here, digital can be the centre point, delivering objective, real-time measures, collecting real-world data and enhancing understanding of patient engagement and adherence. Concurrently, the digital offering can evolve alongside the pharmaceutical, to deliver digital therapy in later-stage trials or as part of a joint commercialisation strategy. At Beats Medical, our platform approach is designed for frictionless deployment in decentralised clinical trials, seamlessly integrating objective digital assessments with enhanced sensitivity, providing a frictionless, streamlined flow of rich data to support pharma’s R&D leaders in delivering more efficient and effective clinical trials.

2. Pharma leaning into RWE and remote clinical trials
Realising the breakthrough potential of digital, pharma will double down on digitally-delivered assessments and outcome measures for clinical trials, and on Real World Evidence generation in early stage Natural History Studies (especially in geographically dispersed patient populations like rare disease) and in post-market surveillance. In December, the FDA published its updated draft guidance on Real-World Evidence to Support Regulatory Decision-Making for Medical Devices. This update replaces the 2017 guidance, where the accepted use of RWD was essentially limited to post-market studies and label expansions. Fast-forward to 2024, and the acceptance of RWE across areas like generating clinical evidence to support marketing authorisations and to support the clinical validation of biomarkers and clinical outcome assessments, means that the runway is clear for pharma to embed digital as primary endpoints in their trials.
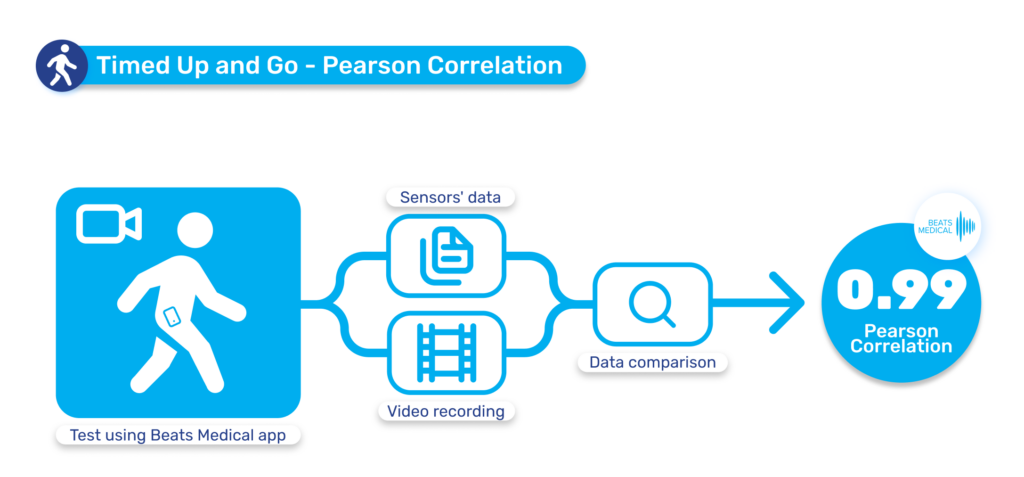
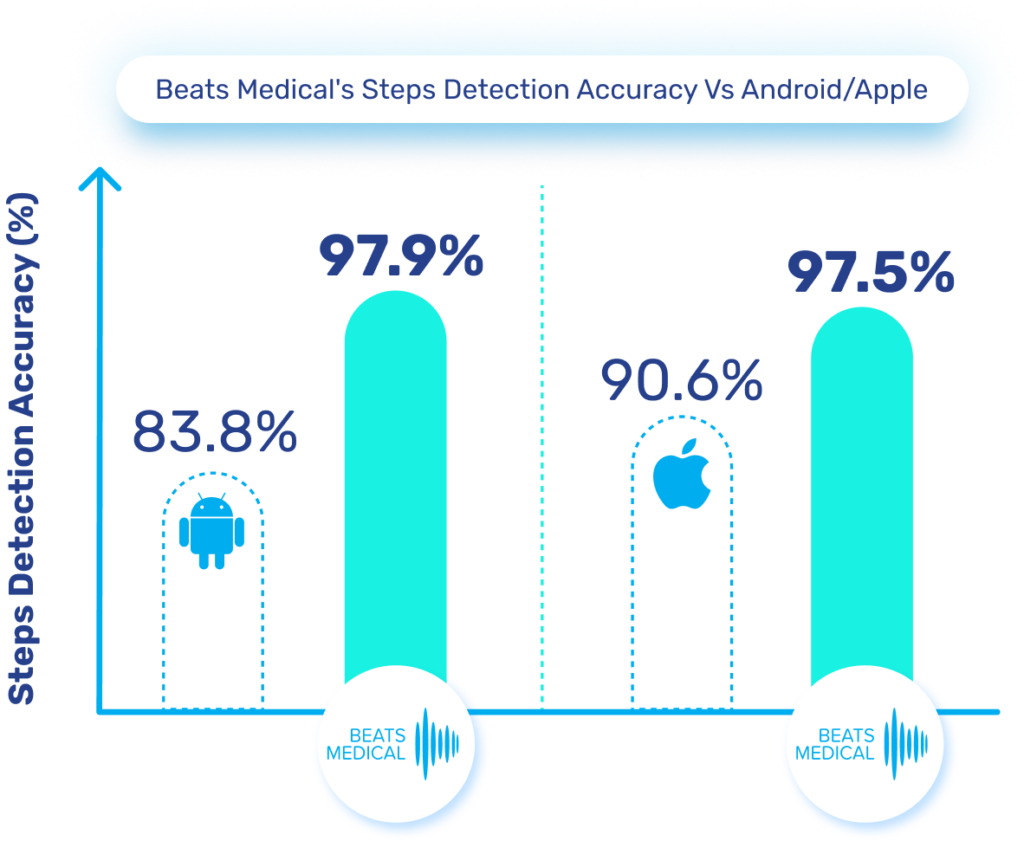
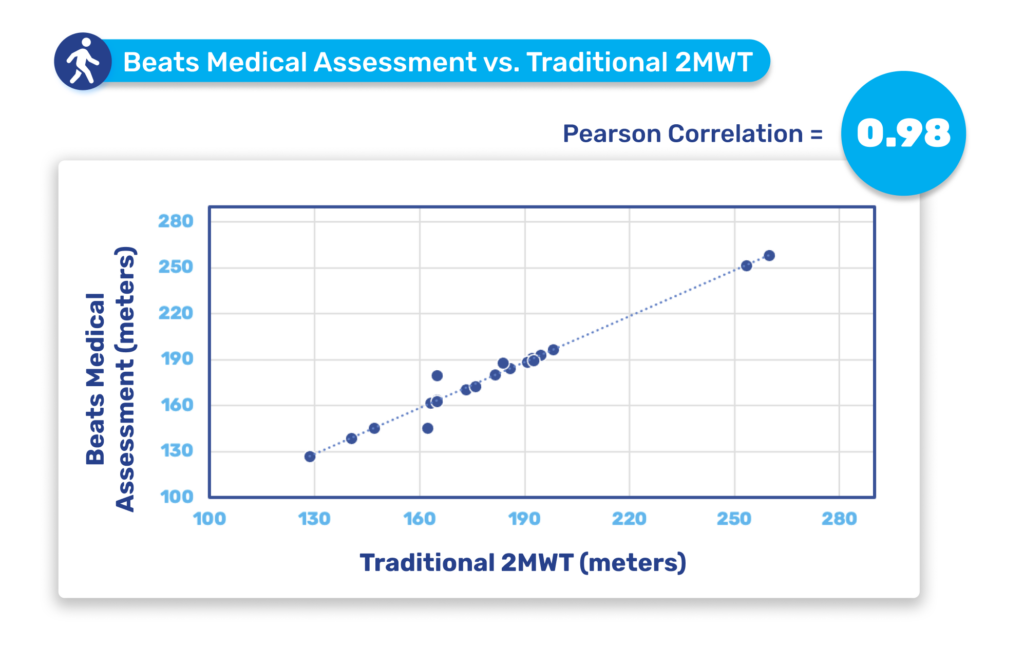
Until now, pharma has been slow to fully leverage digital measures in clinical trials to expedite drug development and enhance participation. Major milestones for digital in clinical trials have been in respiratory and neuromuscular conditions. Oncology is next anticipated to experience a high adoption of digital endpoints, followed also by cardiovascular diseases, and this will only continue to broaden [1]. Mobile phones, being powerful and readily accessible devices, are well-known to both patients and healthcare providers (HCPs). Their inclusion in “bring your own devices” studies is poised to mitigate one of the most significant barriers to adopting digital measures in R&D. In 2024 and beyond, I anticipate more successes like the qualification of the stride velocity 95th centile (SV95C) as an acceptable digital primary endpoint [2]. Naturally, the versatility of digital measures contributes to their appeal in R&D; over time, certain digital endpoints will gradually replace subjective measures, while others will be exclusively deployed in trials to assess disease progression. Delivering these measures in a frictionless way, in a real-world environment, will bring unprecedented participation to pharma trials. The key will be in how ‘frictionless’ this can truly be for patients. For example, the Beats Medical Colbolt platform plays a crucial role in facilitating decentralised clinical trials, leading the market in objective assessments, and most importantly utilising only a mobile phone without the need for additional hardware or sensors (read more about how Beats Medical achieves this here). This facilitates the adoption of digital endpoints by pharmaceutical companies with the broadest possible reach, fast-tracking the discovery of digital biomarkers across various disease areas.

3. GenAI and digital biomarkers – the rise of precision medicine with synthetic data
As remote clinical trials and RWD become the norm, the ability to gather much larger, more robust data becomes a reality. Enter Generative AI. The focus of 2023 was firmly on AI, with the conversation moving from “We use AI” to “Here’s how we’re using AI, here’s how strong our models are, how strong the data they’re trained on is, and here’s how it’s solving our R&D challenges”. The strength of OpenAI’s ChatGPT is its accessibility, and how anyone can use it. But now, pharma must push the capabilities of GenAI to bring value that a generalised platform like ChatGPT can’t.
The integration of AI algorithms in the analysis of digital biomarkers will expedite the discovery of potential drug targets and deepen our understanding of patient responses, streamlining our approach to precision medicine. GenAI has now made it possible to use synthetic data in clinical trials, as a control group replacing placebo arms. This will empower pharmaceutical companies to create diverse datasets for algorithm training without impacting patient privacy or safety. For example in the area of Rare Diseases, where drugs with accelerated approvals can struggle to recruit for post-market studies and maintain the integrity of their placebo groups, synthetic data, paired with objective RWD, can fuel Generative AI platforms to predict risk factors, honing in on treatment response and identifying outliers for deeper exploration. A major hurdle for the widespread use of such synthetic data, and resulting GenAI-powered R&D, will be FDA acceptance. Although the FDA is approaching this space with understandable scrutiny, there is much support in the agency, as shown in their recent publication of two discussion papers on AI in drug discovery.
In 2024, Artificial Intelligence, particularly GenAI, will continue to spearhead discussions on the drug development process. Though deployment will take time due to digital immaturity, accuracy concerns, privacy considerations, regulatory pitfalls, and compliance challenges, as an industry we can be optimistic that real breakthroughs will be achieved sooner than previously expected.

4. Breakthroughs in disease understanding
A final, significant challenge must be addressed for this breakthrough approach to bear fruit: recruiting and retaining a diverse, unbiased clinical trial cohort. Presently, 72% of participants express concerns about the time commitment, and 83% have reservations about the types of procedures involved [5]. Furthermore, in-clinic trials provide a barrier to access for the 20% of the US population who live rurally, with travel and cost constraints impacting the participation of under-served and disadvantaged populations. Adopting a remote clinical trial design will allow previously undetected data insights from patient populations that have traditionally been under-engaged. For example, just 11% of clinical trial participants worldwide are Asian, yet 60% of the global population is Asian. [6] Ultimately, ensuring accessibility and clarity in clinical trial design can reduce barriers to participation and improve diversity and access in patient cohorts. This approach will immerse pharma research teams in the real-world context of patients. Departing from traditional episodic site visits, digital enables a continuous stream of data that reflects patients’ daily lives, behaviors, and crucially their environments. This access to real-world context will enhance our understanding of diseases by providing a holistic perspective that was previously unattainable through isolated site visits.
The confluence of the above trends is a new era characterised by unprecedented breakthroughs in disease understanding. At the heart of this transformative shift lies the impact of state-of-the-art technologies that transcend the conventional boundaries of medical research. While difficult to predict which conditions will benefit most in 2024, it is clear that such breakthroughs can transform our current understanding of complex Central Nervous System conditions and Rare diseases. A deeper understanding of highly complex, heterogeneous conditions can be made possible by technology which facilitates a detailed longitudinal analysis, unveiling patterns, trends, and treatment responses that were previously not apparent. Through GenAI, powered by remote precision data collection, we will be able to subgroup and study neurological conditions like never before, potentially leading to the breakthrough therapies of the future, today.
2024 promises to be a transformative year for pharma, marked by groundbreaking advancements in disease understanding, innovative collaborations, digitised and decentralised trials, and deeper integration of AI within drug development processes. As we embrace these trends, the future of healthcare stands to benefit from more effective trials, unlocking breakthrough treatments, improving patient outcomes, and accelerating drug development timelines exponentially.
Ready to join us on this exciting journey? It’s time to redefine the future of clinical trials, today.
For more information about how we can support your clinical trial pipeline, reach out to me at andrew@beatsmedical.com or on LinkedIn.
References
[1] Unlocking the Value of Digital Measures in Drug Development – November 2023 – HealthXL and Biofourmis
[2] Qualification Opinion for Stride velocity 95th centile as primary endpoint in studies in ambulatory Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy studies – 28 July 2023 EMADOC-1700519818-1127132 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP)
[3] CBInsights State of Digital Health Global Q3 2023 – Global data and analysis on dealmaking, funding, and exits by private market digital health companies
[4] 2024 Safety and Regulatory Compliance Trends and Predictions for Pharma and Biotech – Whitepaper IQVIA
[5] The 2023 WCG Avoca State of the Industry Report – 360º Assessment of the Clinical Trial Industry
[6] Sharma, A., Palaniappan, L. Improving diversity in medical research. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7, 74 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-021-00316-8